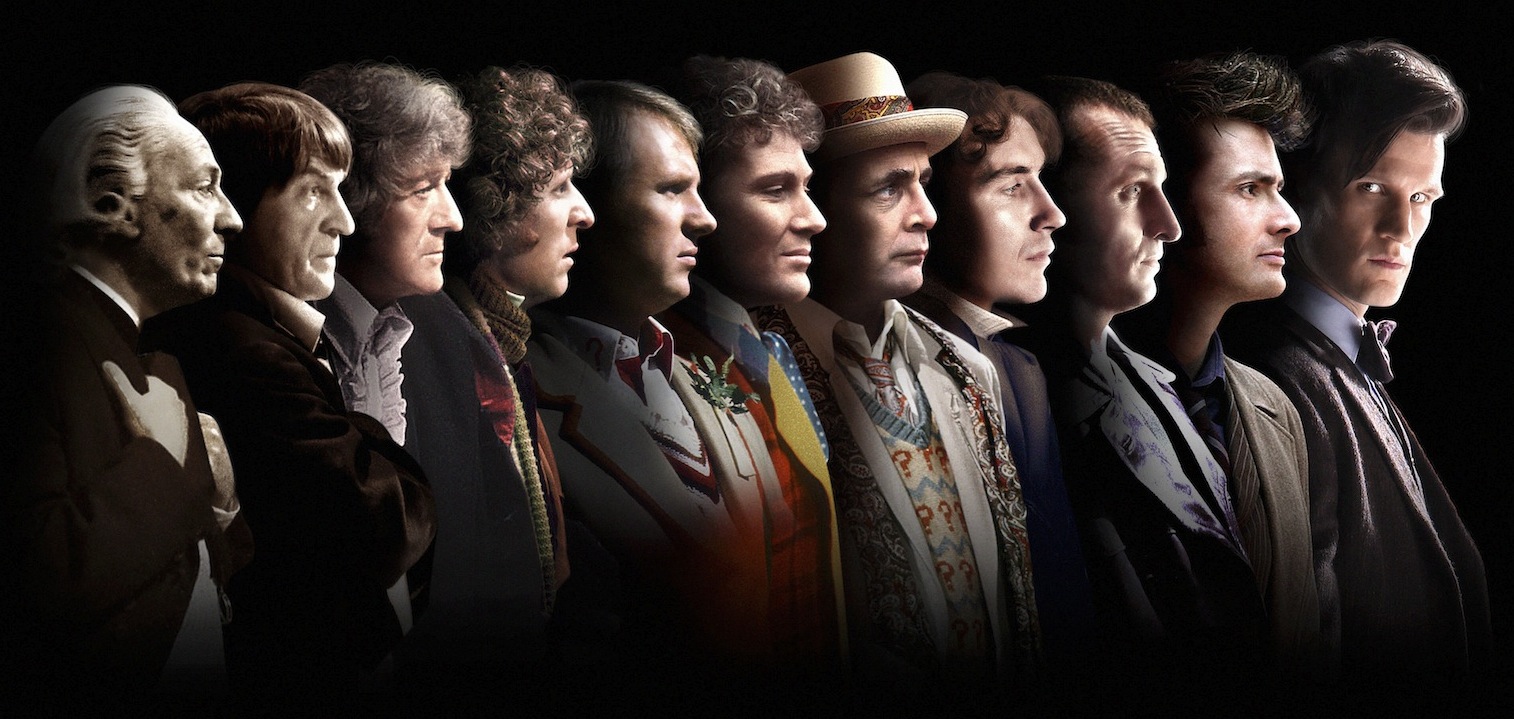
Doctor Who celebrates its 50th anniversary this Saturday, November 23rd.
My geek flag is firmly planted in space science fiction. I became a psychologist because of Star Trek. Firefly helped me understand myself. And I use Battlestar Galactica to teach suicide prevention. When my mind wanders, it gravitates to the final frontier.
Science fiction isn't just about space though. I've grown to love stories about dystopias, robotics, and time-travel too. That's why I was intrigued when BBC relaunched Doctor Who in 2005. I never saw the original Doctor Who series, but I knew it integrated many aspects of science fiction and was beloved around the world.
I made it through 2 episodes of the new Doctor Who series before I quit. I didn’t understand the rules of the universe and was turned off by the cheap visual effects. I love British humor (I grew up watching Mr. Bean and Are you Being Served?) and I'm a huge fan of campy scifi (Galaxy Quest and The Fifth Element are amazing movies), but Doctor Who was just too weird for me.
This was the moment I decided to stop watching Doctor Who.
Even though I gave up on the Doctor, I couldn't quite escape him. My friends pestered me to give the show another chance, readers of this website kept asking me to write about the Doctor, and each time I spoke publicly about the psychology of science fiction someone in the audience ALWAYS brought him up. I read a few Wikipedia articles about Doctor Who, enough to drop references to sonic screwdrivers and the TARDIS. That got me by for a while. But when Geek Therapist Josué Cardona publicly called me out for not understanding Doctor Who on his podcast a couple of weeks ago, it become painfully clear to me that I wouldn't have any credibility as a science fiction psychologist until I understood what made Doctor Who so popular.
The more I learned about Doctor Who, the more it reminded me of other scifi shows that I love. Illustration by J. K. Woodward for IDW Comics.
I reached out to the Whovians in my life and asked them why they cared so much about the show, people like The Memoirist and The Superherologist. They told me about the Doctor's constant spirit of adventure, how he always did the right thing no matter the cost, and his imaginative intellect. That gave me a familiar context for the character – basically a mashup of Indiana Jones, Captain Kirk, and Sherlock Holmes, which sounded awesome! After my buddy, Bill, told me about BBC's tiny budget, I felt like a jerk for judging the show based on its special effects alone. What really hit me was how another friend, Anne, described her interpretation of regeneration – "like the Doctor, we can all shed dysfunctional parts of ourselves, keep our strengths, and build towards a better future." That's the same idea behind Star Trek! The more I listened to people who loved the Doctor, the more familiar he became.
After publicly shaming me, Josué was kind enough to guide me through the best episodes of the show, like "Blink", "Father's Day", and "The 11th Hour". He gave me context and answered my questions. I initially committed to watching only 5 episodes, but now I've seen 17. Sure the order I saw episodes was a bit wibbly wobbly, and I’m still confused about the mythology, but I get the appeal now. As Craig Ferguson said, Doctor Who is about “the victory of intellect and romance over brute force and cynicism.” What’s not to love about that?!?
For a kid who grew up being judged for looking different and having geeky interests, it was stupid for me to reject Doctor Who just because it was unfamiliar. But that’s how our psychology works – we like things we’re used to. The Doctor taught me that the only way to boldly go is by immersing ourselves in the unfamiliar and listening to people who see things differently than we do.